Lean Startup: The Method That Helps Entrepreneurs Succeed Faster

Starting a business often involves a certain degree of uncertainty. How do you know if your idea will work? How can you avoid wasting time and resources on something that may not even be in demand? The Lean Startup method offers an effective and structured approach to tackling these challenges. This guide will show you how to use the method to test, learn, and develop your idea — with minimal risk and maximum potential.
What is Lean Startup?
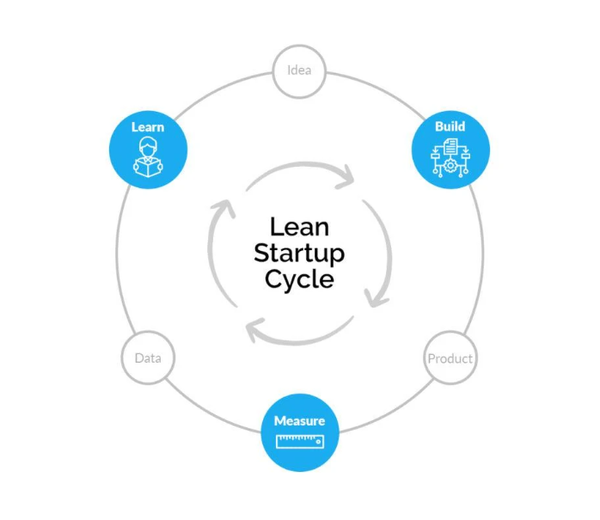
Lean Startup is a method for building and developing businesses by using rapid iteration (repeating and improving a process), customer insights, and continuous learning. It is based on three core principles:
- Build–Measure–Learn Cycle: Focus on quickly creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) that can be tested in the market.
- Validated Learning: Instead of making decisions based on assumptions, rely on data from real customers.
- Rapid Iterations: Development happens in short cycles, with customer feedback guiding the next steps.
How Does the Lean Startup Method Work?
1. Start with a Hypothesis
Every business idea is based on a hypothesis about a problem and its solution. The Lean Startup method suggests identifying:
- Who are your customers?
- What problem are you trying to solve for them?
2. Create a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
An MVP is the simplest version of your product that can still solve the customer's problem. The goal isn’t to create a perfect product but to test your hypothesis. An MVP might include:
- Core Functionality: The most basic features needed to solve the customer’s problem.
- Prototype or Mockup: A simple visual representation of your product.
- Manual Processes: Sometimes, parts of the MVP can be handled manually behind the scenes to test the idea quickly without fully developed systems.
- Feedback Channels: Tools to collect and analyze customer feedback, such as surveys or user behavior analytics.
Example: If your idea is a new tech platform to connect freelancers with companies, your MVP might be an app prototype with only the most essential features, such as a searchable profile and a basic booking function.
3. Test in the Market
Launch your MVP and collect data from real customers. Key questions to answer include:
- Do customers understand the value of your product?
- Does your product solve their problem?
4. Analyze and Iterate
Use the feedback to either:
- Pivot: If your hypothesis proves incorrect, adjust or adapt your product or strategy.
- Persevere: If your hypothesis is validated, move forward with further development and scaling.
Benefits of Lean Startup
- Reduces Risk: Instead of investing large resources in an unproven idea, you build gradually based on customer insights.
- Faster Learning: You get immediate feedback from the market and can adapt quickly.
- Customer-Focused: The method puts customers at the center, increasing the chances of creating a product that meets real demand.
Remember: The key is not to start perfectly, but to start. Your MVP is just the beginning of the journey.
Good luck!